CTE’s Extrusion Technology: Biomass Raw Material Compounds

As industries worldwide shift towards sustainability and decarbonization, biomass raw material compounds have emerged as a viable alternative to petroleum-based materials. Derived from renewable sources like wood, starch, and cellulose, these materials play a pivotal role in reducing environmental impact while supporting sustainable production practices.
This article highlights how CTE’s cutting-edge extrusion technology addresses the unique challenges of processing biomass raw materials, ensuring consistent and high-quality compounding results.
Challenges in Biomass Raw Material Compounding and CTE’s Solution
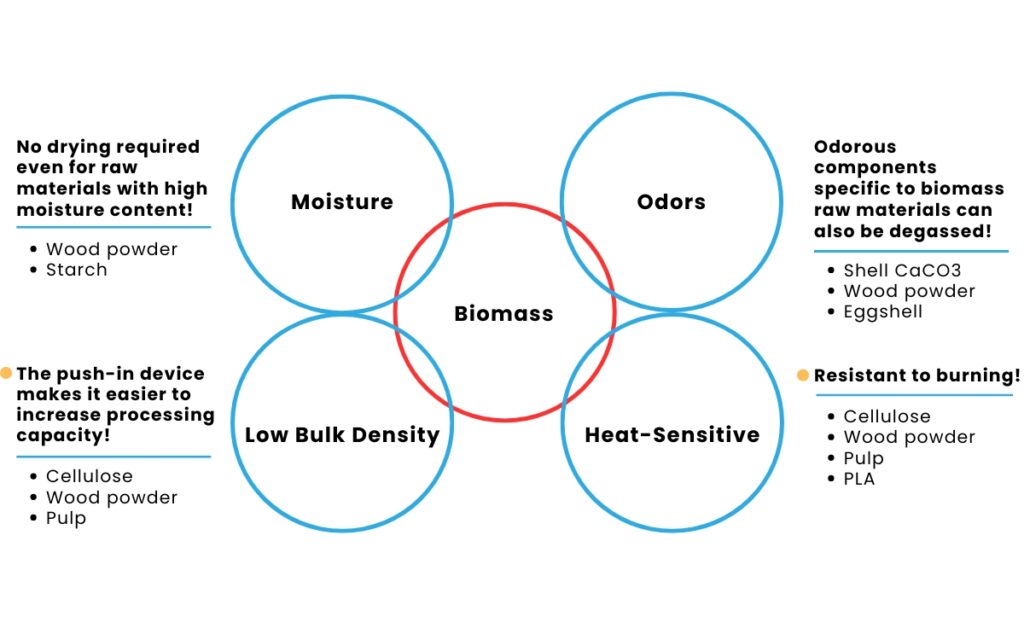
Biomass raw materials such as wood flour, cellulose, and starch have inherent characteristics that complicate their processing:
・Low bulk density, which can hinder consistent feeding.
・High moisture content, leading to issues like poor flow and degradation.
・Heat sensitivity, which increases the risk of material damage during compounding.
・Odor challenges, due to volatile components.
Traditional intermeshing co-rotating twin-screw extruders often struggle with these issues, resulting in inconsistent throughput and poor compound quality.
To address these challenges, CTE’s HTM Non-Intermeshing, Counter-Rotating Twin-Screw Extruder offers a specialized solution. Its unique design ensures stable and efficient compounding of biomass raw materials, even in demanding conditions:
Degassing capability eliminates excess moisture and volatile components.
Consistent feeding mechanisms handle low-density materials without blockages.
Heat minimization during kneading preserves the integrity of heat-sensitive materials.
Key Features of HTM Twin-Screw Extruder for Biomass Compounding
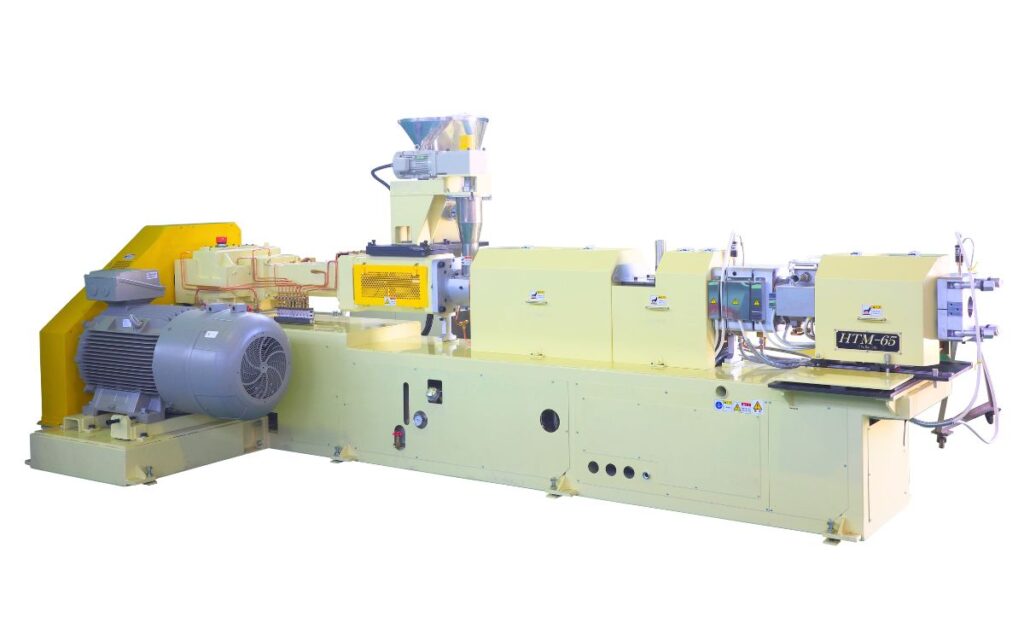

・Advanced Degassing Performance: The non-intermeshing screws effectively remove moisture and odors, ensuring better material consistency.
・Optimized Feeding System: Specialized mechanisms prevent feed interruptions and maintain stable throughput for low-density materials.
・Minimized Thermal Impact: Innovative rotor elements reduce heat generation during kneading, enabling processing of even heat-sensitive biomass raw materials.
CTE’s HTM Twin-Screw Extruder has been successfully applied to process a range of biomass raw materials, transforming them into high-quality compounds for diverse industrial applications. Examples include:
Examples of Biomass Raw Material Compounds
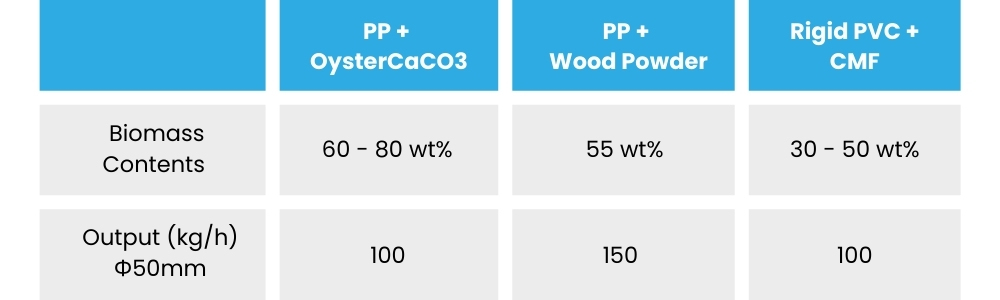
Wood Flour Compounds: Used in sustainable plastic composites.
Cellulose Compounds: Applied in biodegradable packaging materials.
Starch-Based Compounds: Ideal for renewable bioplastics.
These applications demonstrate the HTM extruder’s versatility and reliability in supporting sustainable manufacturing practices.
Conclusion
Biomass raw material compounding presents unique challenges, but CTE’s HTM Twin-Screw Extruder offers a groundbreaking solution. By enabling efficient processing, enhanced throughput, and superior compound quality, our extrusion technology paves the way for innovations in renewable materials.
At CTE, we are dedicated to advancing sustainable manufacturing with industry-leading extrusion solutions. Explore the potential of biomass raw material compounds and join us in shaping a greener future.